Network security is the practice of protecting computer systems and networks from digital threats. Securing our networks becomes more critical as we continue to rely on the internet for work, shopping, banking, and staying connected. Cybercriminals are constantly looking for weaknesses to exploit, which can lead to stolen data, financial losses, or even business shutdowns. This blog post delves into the importance of network security, common threats, and how you can protect your network from potential attacks.
What is Network Security?
Network security is the process of protecting a network from unauthorized access, misuse, or attacks. The goal is to ensure that the information sent over a network remains private and intact. Network security includes hardware and software components that protect your network from cyber threats like viruses, malware, and hackers.
Network security involves measures such as firewalls, encryption, and secure passwords. In essence, it safeguards data from being accessed or corrupted by cybercriminals and keeps systems functioning as they should.
đź‘Ť Get Stunning Lifetime Access Now!
Why is Network Security Important?
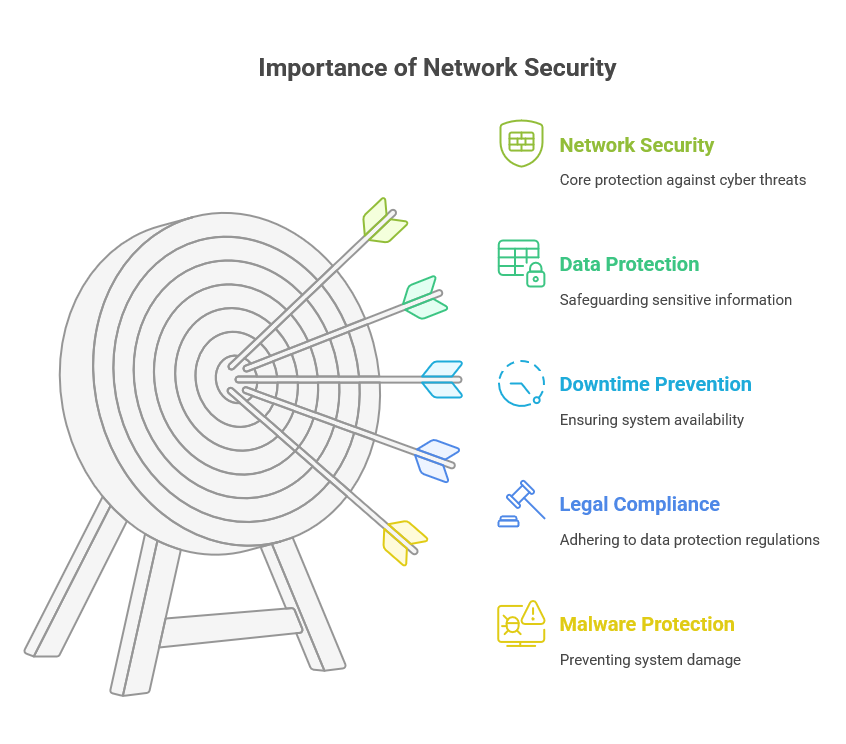
With the rise in cybercrime, network security has become a top priority for individuals and businesses. Here’s why network security matters:
-
Protects Sensitive Data: Sensitive information such as financial records, personal data, and private business information needs to be protected. A data breach can lead to identity theft, fraud, or the loss of valuable intellectual property.
-
Prevents Downtime: Cyberattacks, especially denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, can cause businesses to lose access to their websites or systems. This leads to downtime, which can be costly and hurt a company’s reputation.
-
Avoids Legal and Financial Consequences: Data breaches and security lapses can result in legal penalties and hefty fines, especially if your business fails to comply with data protection regulations.
-
Protects Against Malware: Malware can cause massive damage to individual and business systems. By keeping this type of software at bay, network security helps prevent system crashes and data loss.
Common Network Security Threats
Understanding the types of threats you may face can help you take steps to protect your network. Here are some of the most common threats to watch out for:
1. Malware
Malware refers to any malicious software designed to harm your computer system. It includes viruses, worms, and ransomware. Once installed on a device, malware can steal personal information, monitor activities, or lock you out of your system until you pay a ransom.
The best way to prevent malware attacks is to install up-to-date antivirus software and avoid downloading files or software from unreliable sources.
2. Phishing
Phishing is a technique cybercriminals use to trick people into sharing sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details. It usually involves fake emails or websites that appear legitimate. Phishing attacks prey on people’s trust, making them click on malicious links or attachments.
You can protect yourself from phishing by avoiding unsolicited emails and never entering personal details on a website unless you’re sure it’s secure.
3. Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
A DoS attack floods a network with excessive traffic, overwhelming its resources and causing it to crash. In some cases, the attacker demands a ransom to stop the attack. For businesses, these attacks can lead to website downtime and a loss of revenue.
Protecting your network from DoS attacks requires firewalls, monitoring tools, and strategies to identify and block malicious traffic.
4. Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks
In a MITM attack, a hacker intercepts and alters communication between two parties. This could mean an attacker listening in on your conversations or manipulating the data you send. MITM attacks can happen over unsecured public Wi-Fi networks.
You can defend against MITM attacks by using encryption tools and virtual private networks (VPNs), and you can ensure your connection is secure when using public networks.
5. Ransomware
Ransomware is malware that locks your files or entire system and demands payment to release them. These attacks are hazardous for businesses, as they can shut down operations altogether.
Ransomware attacks can be prevented by regularly backing up data, updating software, and using robust security software that detects threats before they cause harm.
Best Practices for Network Security
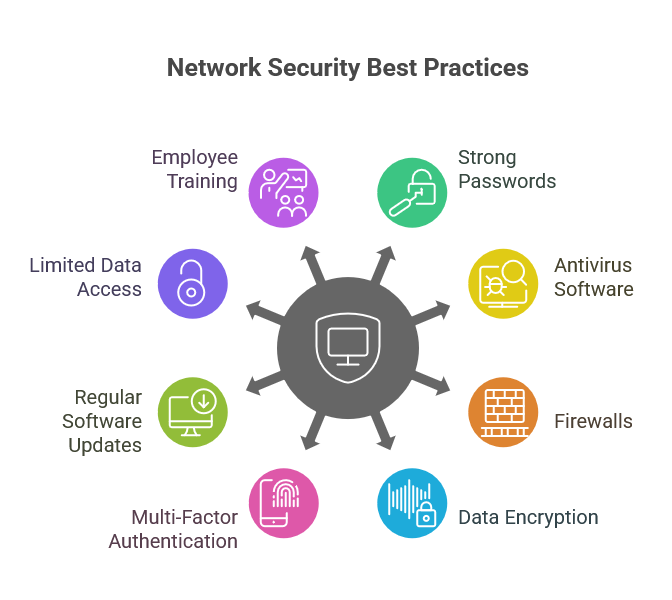
To protect your network from potential threats, follow these best practices:
1. Use Strong Passwords
Weak passwords are one of the easiest ways for hackers to access your network. Create complex passwords that include a mix of upper- and lower-case letters, numbers, and symbols. Also, avoid using the same password for multiple accounts.
Use password managers to store and generate secure passwords.
2. Install Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
Antivirus software can detect and remove malicious software before it infects your system. Keep your antivirus software current and run regular scans to check for threats.
3. Enable Firewalls
Firewalls act as a barrier between your network and the outside world. They monitor incoming and outgoing traffic, blocking anything suspicious. Make sure you have firewalls enabled on your devices and network.
4. Encrypt Your Data
Data encryption makes it unreadable to anyone who does not have the proper decryption key. Whether on your hard drive or while transmitting over a network, encryption ensures your sensitive data stays secure.
5. Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring more than just a password to access your account. This could be a fingerprint scan, a code sent to your phone, or a face scan. Using MFA reduces the chances of unauthorized access, even if your password is compromised.
6. Regularly Update Software
Hackers often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software. Regularly updating your operating system, applications, and antivirus software helps fix known vulnerabilities. Many programs allow you to enable automatic updates to ensure your software is always current.
7. Limit Access to Sensitive Data
Not everyone in your organization needs access to sensitive data. Limit access to only those who require it to perform their duties. This reduces the chances of data leaks or internal breaches.
8. Train Employees
If you have a business, ensure your employees know basic security protocols. Educate them about phishing, safe browsing practices, and how to identify suspicious activity.
Network Security Solutions for Businesses
Businesses face higher risks due to the vast amount of sensitive data they handle. Here are a few security solutions businesses should consider:
1. Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A VPN creates a secure, encrypted connection between remote users and the company network. It allows employees to access business resources safely, even when working from home or traveling.
2. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
An IDS monitors network traffic for suspicious activity. It can alert you in real time when a potential attack is detected, allowing you to take immediate action.
3. Endpoint Protection
Endpoint protection ensures that devices connected to your network, such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets, are secure. This includes installing antivirus software, firewalls, and encryption on all devices.
4. Cloud Security
Many businesses store sensitive data in the cloud. Cloud security solutions protect this data from cyberattacks and unauthorized access, ensuring your business’s digital assets remain safe.
The Cost of Poor Network Security
The financial and reputational costs of a network breach can be significant. According to IBM, the average price of a data breach in 2020 was $3.86 million. For small businesses, this could be disastrous. Not only do you lose valuable data, but the attack can result in lost customers, lawsuits, and regulatory fines.
Statistics on Network Security
Here are some eye-opening statistics about the state of network security:
-
Cybercrime costs businesses: Cybercrime will cost businesses over $10 trillion annually by 2025 (Cybersecurity Ventures).
-
Phishing attacks are the most common, involving around 32% of data breaches (Verizon’s 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report).
-
Ransomware attacks are rising: Ransomware attacks grew by 300% in 2020 (Cybersecurity Ventures).
FAQs on Network Security
1. What is the best way to secure my home network?
Use strong passwords, enable a firewall, install antivirus software, and keep your devices updated.
2. How can I secure my business network?
Use VPNs, firewalls, encryption, endpoint protection, and train employees on good security practices.
3. Why should I use a VPN?
A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, providing secure remote access and protecting your data from hackers.
4. What are some common signs of a cyberattack?
Slow network performance, unexpected pop-up messages, or strange system behavior could be signs of an attack.
5. How often should I update my antivirus software?
Ensure your antivirus software is always up to date to detect the latest threats. If possible, set it to update automatically.
Network security isn’t a one-time task. It requires ongoing effort, regular updates, and vigilance. The more proactive you are about securing your network, the less likely you are to fall victim to cyberattacks. Whether you’re an individual or a business, implementing strong network security practices is essential to protecting your data, privacy, and overall digital well-being.

